What to use to judge the quality of a cotton yarn? What kind of cotton yarn is really good cotton yarn? Take a few minutes to look at the quality standards of cotton yarn.
First, the quality standard and quality inspection of cotton yarn
1, cotton yarn quality indicators
The traditional spot trade indicators of cotton yarn mainly include: linear density, variation coefficient of strip evenness, single yarn breaking strength, single yarn breaking strength variation coefficient, 100m weight deviation, 100m weight variation coefficient, -50% kilometer detail, + 50% kilometer thick, +200% kilograms neps, 100,000 meters gauze, hairiness and so on.
Line density: The number of yarns, refers to the quality of the yarn per unit length, used to indicate the degree of thickness of the yarn, directly related to the final product type, use and physical and mechanical properties.
Coefficient of variation of dryness uniformity: It indicates the unevenness of short-length yarns within a certain length, which is a comprehensive expression of the technological and mechanical factors of the spinning production system, and is also the most important quality index in the cotton yarn trade.
100m weight deviation: It is the deviation between the actual dry weight of the yarn and the designed dry weight, which reflects the deviation of the actually spun yarn from the yarn density required by the design. Therefore, the weight deviation and weight variation coefficient detected together with the line density are important quality indicators and are directly related to the interests of manufacturers and users.
Single yarn breaking strength, single yarn breaking strength coefficient of variation: Due to the presence of various yarn irregularities, under the influence of external forces tend to break in the weakest link, so for the later high-speed weaving, the yarn is required to have a certain The strength and average strength.
-50% kilometer details, +50% kilometer thick, +200% kilograms of neps: is an indefinite point, measured in kilometer; its size and quantity will influence the quality of downstream processing to varying degrees. Fabric appearance. Generally, it is caused by abnormal factors such as process parameters, sudden changes in temperature and humidity, raw materials, etc. (more miscellaneous, high short fiber rate, poor length uniformity, and insufficient maturity).
One hundred thousand meters of gauze: It is a sudden defect, referring to the sudden occurrence of a large area affecting the cotton gauze down; the characteristics of ferocious and bulky, seriously affect the quality of cotton. It is generally caused by mechanical parts and equipment that are not cleaned up in time, raw materials fluctuate, and sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
Hairiness: Fibers are formed on the surface of the yarn body during yarn formation. The hairiness of the cotton yarn directly affects the weaving efficiency, fabric style and dyeing effect: less hairiness can make the fabric surface fine, clean, slippery, cool, soft to the touch, elastic and full of textured; more hairiness can make the surface of the fabric fluffy Feeling, but more than 3mm hairiness will easily lead to tangled yarn, more broken ends, decreased weaving efficiency; severe hairiness uneven will make the cloth to form cloud spots, cross file and other defects, affecting the quality of printing and dyeing and appearance quality.
2. The main quality inspection standards of China's cotton yarn - cotton yarn yarn GB
The "National Standard Cotton Yarn of the People's Republic of China" (GB/T 398) was issued by the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine and the National Standardization Administration. The latest version was implemented on December 1, 2008. This standard is based on the statistical value of ring-spinning mechanism cotton natural yarns, and stipulates its product classification, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules and signs, and packaging.
The standard stipulates that a batch of production of the same variety for a day and night shall be tested in accordance with the specified test cycle and various test methods, and the products of cotton yarn shall be evaluated according to the results. The products of cotton yarn are classified into excellent, first-class and second-class, and those below the second-class index are third-class. At present, in the domestic spot market, the trade volume of cotton yarns at or above the first level accounts for the largest proportion, accounting for about 90%; among them, the proportion of excellence is as high as 20%.
The standard also stipulates that cotton yarns, etc., from single yarn breaking strength coefficient of variation, 100m weight coefficient of variation, single yarn breaking strength, 100m weight deviation, coefficient of variation of evenness of strips, 1g of cotton nuggets, 1g of inner neps The lowest one of the total number of impurities and one of the eight hundred thousand meters of yarn.
3. The main international cotton yarn quality inspection standards - Uster Bulletin
The Uster Bulletin is a quality grading reference for the classification of fibers, strips, rovings and yarns in the textile industry worldwide. It is used as a general measure of quality control and commercial price positioning. It is Uster's testing of fibers, semi-finished products and spun yarns in users all over the world and in factories in Switzerland. It then performs data compilation and analysis to obtain the quality of yarns and cotton fibers in different specifications worldwide. Level. The statistical values ​​of the test results, namely USTER statistics, are divided into 5%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 95% bins. It is generally believed that 50% of the statistics are at normal levels, 25% and below are advanced levels, and 75% and above are at poor levels. Uster statistics are dynamic and are published every 3-5 years.
Uster Bulletin 2007 Sample Source Area Distribution Map
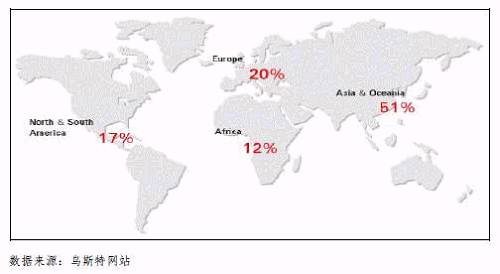
However, the quality of the yarn can not be completely judged by the Ust Communique, but it must be judged by the effect of the test fabric. Different customers have different emphasis on the indicators, such as woven yarn customers controlling the coarse section, nep, 100,000 m yarn defect, strength and strength coefficient of variation index level, other indicators can be appropriately relaxed; knitting yarn customers are strictly required The level of indicators such as details, degree, hairiness and other indicators may be appropriately relaxed.
4. Cotton yarn quality inspection
Cotton yarn quality inspection can be divided into three ways: state agency inspection, enterprise self-inspection and third-party inspection. Because the inspection method is simple, the quality inspection of spot trading cotton yarns is mostly based on self-inspection by enterprises; the relevant state departments perform unscheduled sampling tasks on cotton spinning products by state agencies; while most of the quality inspection tasks for trade disputes are performed by the state. Institutions and third-party agencies undertake.
At present, China has built six national textile and clothing quality inspection centers, including Shanghai, Tianjin, Guangzhou, Zhejiang, Fujian and Henan. Among them, Henan and Shanghai's state-level textile and clothing quality inspection centers focus on the detection of cotton yarn and cotton textiles, Zhejiang and Fujian focus on chemical fiber textile testing, and Guangzhou focuses on textile and clothing testing. In addition, most provinces and districts have textile (fibular, state) grade fiber inspection agencies in most of the main production areas and sales areas of textile fibers. Relevant inspection agencies are fully equipped and operate, and they have all levels of qualification certification and management systems.
Second, the transport of cotton yarn
The transportation of cotton yarn is divided into domestic transportation and import and export transportation. Domestic transportation mainly consists of automobile road transport, and import and export transport uses container shipping.
1. Domestic transportation
Due to the concentration of China's cotton yarn production and sales regions, automobile transportation has become the most commonly used and most economical way. The transportation volume accounts for about 90% of the total cotton yarn transport in China. According to the survey data, the domestic car capacity for cotton yarns varies from 17 to 40 tons/vehicle, depending on the transport distance.
Cotton Yarn Transportation Classification and Features
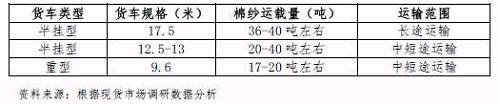
Cotton yarn transport can ensure high transport efficiency and greatly reduce transport time. With Changzhou, Jiangsu as the hub, it takes 3-5 days for Xinjiang cotton yarns to be shipped to Changzhou. It takes only 4 hours from Changzhou to Shandong, Henan and Hubei.
2. Import and export transportation
In general, cotton yarn import volume is relatively large, and the time requirement is not high. Container shipping is often used to save transportation costs. When import volume is low, marine bulk cargo will be consolidated; when the import volume is large, the entire container will be shipped.
In domestic ports, the order of imports of cotton yarns in descending order is: Shanghai Port, Guangzhou Port, Ningbo Port (601018, stock bar), Qingdao Port, Tianjin Port (600,717, stock bar), and Zhangjiagang. Among them, the cotton yarns imported from Shanghai Port are mostly 32 woven cotton yarns, which are mainly supplied to yarns in Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, and other surrounding areas; Guangzhou-based cotton yarns are mainly based on 8-16 cotton yarns (Siro spinning); Ningbo Port Imported cotton yarn is mainly composed of 21 and 32 knitted carded cotton yarns, which mainly supply yarns from Ningbo, Shaoxing and other areas in Jiangsu and Zhejiang.
Source: Zhengzhou
For more content, please follow this site
Boiled Wool Fabric,Boiled Wool,Boiled Wool Coating Fabric,Boiled Wool Knit Fabric
Jiangyin Xiangxu Textile Co., Ltd. , https://www.fabricxiangxu.com