Printing and dyeing wastewater is a kind of wastewater with high organic content, high chroma and difficult biodegradation, and it is one of the problems in wastewater treatment. In recent years, with the development of chemical fiber fabrics, the rise of simulation technology and the advancement of printing and dyeing finishing technology, PVA pulp, rayon alkaline hydrolysate, new auxiliaries and other organic substances that are difficult to biodegrade have entered the printing and dyeing wastewater in large quantities, and their COD concentration By 2000-3000mg/L, the removal rate of the original biological treatment system has dropped from 70% to about 50%. Even lower. Therefore, research on economical and effective printing and dyeing wastewater treatment technology has become an important issue and necessity for environmental protection today [1-3].
1 Summary of treatment methods for printing and dyeing wastewater
Printing and dyeing wastewater treatment methods mainly include physical and chemical methods and biological methods. In the physicochemical method, an adsorption method is commonly used, which is a method in which one or more substances in the wastewater are adsorbed on a solid surface by using a solid substance of a plurality of substances. The adsorbents commonly used in the industry are activated carbon, etc., which are very effective for removing dissolved organic substances in water, but cannot remove colloidal hydrophobic dyes in water [4]. The coagulation sedimentation method can reduce the color of the printing and dyeing wastewater and remove the dye in a colloidal state. Commonly used coagulants are divided into inorganic salts (such as aluminum sulfate, alum, ferric chloride, etc.) and polymer coagulants (such as basic aluminum chloride, polyacrylic acid saddle PAM); air floatation method for printing and dyeing wastewater It contains colloidal particles of the machine, various oily and fat impurities in the form of opacification, fine fibers and cilia of hydrophobic synthetic fibers, etc., and the coagulation agent is used for coagulation in advance, so that the separation effect is better; the electrolysis method is mostly used for treatment. Cyanide-containing and chromium-containing electroplating wastewater has been used in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater in recent years. The decolorization effect of this method is remarkable, the sludge production is small, the treatment time is short, but the power consumption and electrode material consumption are large, and it is suitable for small-water wastewater treatment. The oxidative decolorization method can be used for further decolorization treatment of effluent which has deep color after treatment by biological method and coagulation method, and mainly includes chlorine oxidation method, ozonation method and photooxidation method. In the biological treatment method, the anaerobic method has the advantages of wide range, low energy consumption, less residual sludge, and strong impact load resistance. The disadvantage is that the starting time of the equipment is long, and the effluent water quality cannot meet the standard, and further treatment is needed. The activated sludge process is a main method of aerobic biological treatment, which utilizes the adsorption and oxidation of activated sludge to remove organic pollutants from wastewater. The biofilm method is another aerobic biological treatment method in parallel with the activated sludge method. The method treats wastewater by a biofilm grown on a surface of a filler such as a filter material or a disk surface, and mainly has a biological contact oxidation method and a biological turntable. And biochar method.
2 Project examples
2.1 Water quality and quantity of printing and dyeing wastewater from a printing and dyeing plant in the Pearl River Delta. The treatment scale is 36,000 m / d. The design of influent water quality and effluent is shown in Table 1. The effluent requirement meets the first-level standard of the second period in the “Guangdong Provincial Local Standard Water Pollutant Emission Limit†(DB44/26-2001). 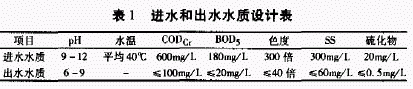
2.2 Process
Conventional treatment methods for printing and dyeing wastewater are generally divided into biochemical + physicochemical and physicochemical + biochemical treatment processes. However, due to the lack of hydrolysis acidification unit, there is a problem that the aerobic biochemical unit reaction is not thorough enough in actual operation, resulting in high cost of subsequent physical treatment. . In the traditional aerobic biological treatment device, the "hydrolysis + aerobic" series process of hydrolysis and acidification is added to hydrolyze the organic matter that is difficult to degrade in the printing and dyeing wastewater, thereby forming a biodegradable substance and improving the biodegradability of the wastewater. Degradability, thereby increasing the COD removal rate of traditional processes. At present, many new printing and dyeing wastewater treatment devices (including domestic sewage and printing and dyeing wastewater centralized treatment) use the “hydrolysis-aerobic†biological treatment process developed by this process, and have achieved obvious environmental and economic benefits.
According to the above analysis, combined with the actual situation, the integrated sewage treatment process is shown in Figure 1. 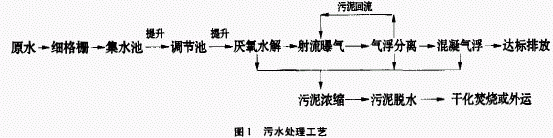
2.2.1 Anaerobic hydrolysis
Dyes are a kind of synthetic organic matter that is difficult to degrade. Its molecular structure mainly contains electron-inducing groups that are difficult to biodegrade, such as azo groups. If the electron-withdrawing substituent on the molecular structure can be removed, and the electron double-stranded or the like is broken, subsequent biodegradation can be easily performed, and the dye molecule also loses the chromophoric group. The mechanism of hydrolysis acidification to degrade dye organic matter and decolorization is to break the electronic double strand of the azo group by the enzymatic action of the hydrolyzed acidified microorganism. This biodegradation process requires the participation of multiple enzymes. Hydrolysis during hydrolysis
The bacteria of Pseudomonas, Aeromonas, and Rhodospirillum grown in the sludge have good decolorization ability. The decolorization ability of the mixed bacteria group is higher than that of each single strain, and the mixed bacteria group relies on synergistic action to make the degradation of the dye more complete and the decolorization more complete.
Hydrolytic acidification treatment can buffer and reduce the pH value of raw sewage, increase the specific gravity of soluble COD in sewage, thereby improve the COD removal rate of subsequent aerobic treatment, and also buffer and adjust the impact of possible impact load, prevent and overcome Sludge swelling or excessive growth of filamentous bacteria may occur during subsequent activated sludge treatment to enhance the stability and reliability of the treatment system.
2.2.2 Jet aeration
The key equipment of the aerobic biochemical system is the oxygenation system. The jet aeration overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional jet aerator with high energy consumption and low power efficiency, greatly improving the oxygenation capacity and reducing the power consumption; avoiding the high pressure blower The noise pollution caused by the elimination of the surface active substance in the sewage has an effect on the oxygen transmission rate, and the oxygen transmission rate is greatly improved; the stroke range of the downward injection can reach more than 10 m, so the depth of the pool can be up to 10 to 14 m, which not only saves The floor space and the energy provided by the water pump and the fan can be fully utilized; the cutting is flexible and convenient.
2.2.3 Air flotation separation
Air floatation water purification technology is a fast and efficient new method for separation of the same liquid in the field of water treatment. It relies on the involvement of numerous microbubbles in the water to adhere to the impurities in the water, causing its overall specific gravity to be less than water and floating up to the surface of the water, thereby achieving separation of the same liquid.
Pressure dissolved air floatation is a condition in which the air is dissolved in water and supersaturated under a certain pressure, and then the water is suddenly reduced to normal pressure. At this time, the air dissolved in the water is in the form of tiny bubbles. The method of escaping in water to complete the air flotation process. The bubble formed by the dissolved air float has a small particle size, and its initial particle size is about 1 to 01. ~m or so. The contact time of the bubbles with water can be controlled as needed. Therefore, the purification efficiency of the dissolved air float is high.
2.2.4 Coagulation and air flotation
Printing and dyeing wastewater is less biodegradable, and it is generally difficult to meet emission requirements by relying solely on biochemical treatment. In order to ensure the final discharge of water to achieve standard discharge, and in order to prevent biochemical system accidents, add a physicochemical process after the biochemical system. The residual color in the waste water is removed by adding a coagulant or a decolorizing agent, and the colloidal substance can be converted into a suspended matter and separated from the water together with the remaining smaller and lighter suspended matter in the waste water. It can also remove some of the bacterial metabolites to ensure the best treatment results. The separation after dosing and coagulation has two kinds of precipitation and air flotation. Among them, the pressurized dissolved air flotation method has better decolorization effect on the treatment of dyeing wastewater. In addition, because the air flotation separation capacity is about 4 to 5 times of the separation separation capacity, the area of ​​the separation zone can be greatly reduced, a large investment is saved, and the separation effect is stable, and is not affected by the external environment.
Select the pressurized dissolved air flotation method as a measure of physical and chemical treatment.
2.3 Main structures
The main structures are shown in Table 2. 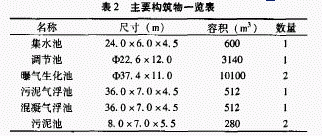
Anaerobic hydrolysis reactors can be divided into three categories: anaerobic activated sludge process, anaerobic biofilm process, and comprehensive method. Due to the large amount of water, the anaerobic biofilm method requires a large amount of filler, which greatly increases the investment cost. Because the water concentration is not high, the anaerobic activated sludge method alone makes the commissioning time long, and it is impossible to avoid sudden muddyping. Taking into account the above factors, the combined (UBF) reactor combined with anaerobic activated sludge process and anaerobic biofilm method can bring the advantages of anaerobic filter (AF) and anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) to improve. running result. The hydraulic retention time is controlled within 10 hours.
The aerobic reactor is two qb37.4×11.0m aerated biochemical pools with a water depth of 10.5m and a total effective volume of 20000m'. According to the daily treatment of 36,000m, the hydraulic retention time is 13h, which can meet the requirements. Processing requirements.
Air floatation is divided into two units: activated sludge air flotation and coagulation air flotation. The operation effect of the former determines the sludge concentration of the aeration tank, and the operation effect of the latter determines the water quality of the final effluent. At present, pressurized dissolved air flotation is the most commonly used air flotation method at home and abroad. The pressure dissolved air flotation process is mainly composed of a pressure dissolved gas system, a dissolved gas release system and an air flotation separation system.
Pressure dissolved gas systems include pumps, air compressors, pressure dissolved gas tanks, and other ancillary equipment. Among them, the pressure dissolved gas tank is the key equipment that affects the dissolved gas effect. At present, the most widely used air compressor is air supply. The air float method requires less air, and an air compressor with a small power can be used to open the intermittent operation mode. In addition, air supply to the air compressor can also ensure that the pressure of the pump does not cause large losses. Generally, the pressure from the pump to the dissolved gas tank is about 0.5 MPa, so energy consumption can be saved. In order to improve the efficiency of dissolved gas, most of them use spray filler pressure dissolved gas tanks.
The dissolved gas release system is generally composed of a release device (or a perforated pipe, a pressure reducing valve) and a dissolved gas water pipe. The function of the dissolved gas release device is to pass the pressure dissolved water through energy dissipation and decompression, so that the gas dissolved in the water is released as microbubbles, and can quickly and uniformly adhere to the impurities in the water.
The main process parameters of the dissolved gas release device are: the flow rate of the pipe before the release: 1 m/s or less, and the outlet flow rate of the releaser is O. 4—0.5m/s is suitable: the opening degree of the narrow gap during washing is 5mm; the range of each release is 30-100em. Air flotation separation system. Generally can be divided into advection, vertical flow and integrated. Its function is to ensure a certain volume and the surface area of ​​the pool, so that the microbubble group and the floc in the water are fully mixed, contacted and adhered to ensure separation of the gas floc and the clean water.
2.4 Operational technical requirements and results 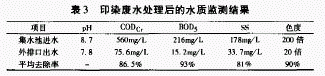
The results of water quality monitoring at 3 months of operation are shown in Table 3 (average). According to the monitoring results, the effluent water quality is superior to the first-level standard of the second period in the “Guangdong Provincial Local Standard Water Pollutant Emission Limit†(DB44/26-2001).
3 Conclusions and recommendations
(1) Practice has proved that anaerobic hydrolysis + jet aeration + air flotation reflux + coagulation air flotation process has a good effect on the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater.
(2) Temperature is an important factor affecting the biodegradability of wastewater. After analyzing the change of wastewater water temperature, the average water temperature of the inlet tank is 40~C, which will still affect the treatment effect of the biochemical system. Therefore, the wastewater needs to be reduced to 38. °C can enter the hydrolysis acidification tank.
(3) Printing and dyeing wastewater Due to the difficult biodegradability of some dyes, the B/C ratio is not very high, generally about 0.3, and the wastewater is hydrolyzed and acidified in an anaerobic hydrolysis tank. The C ratio can be increased to about 0.35.
(4) In printing and dyeing wastewater, sulfide concentration and sulfate concentration will affect the biodegradability of wastewater. When the sulfide concentration is lower than 20mg/L, it will not inhibit the biochemical reaction of acidified bacteria and aerobic bacteria. The effect of sulfate on the biochemical system is mainly due to its reduction to inhibitory hydrogen sulfide under the action of anaerobic bacteria, but its concentration within lg/L does not have a great impact on the biochemical system. In addition, the hydrolysis acidification tank The residence time should be shorter, and the anaerobic bacteria will not become the dominant microorganisms, so as to ensure that the sulfate concentration will not affect the biochemical system.
home textile, back cushion, bedding, blankets, quilting quilt, towel, memory foam pillow and cushion, the gloves for kitchen, the pat
Nanjing Intime Import and Export co., Ltd. , https://www.njireneintime.com